Magnesium for sleep is not merely a folk remedy; it is a scientifically validated nutritional strategy for achieving deep, restorative rest. In our high-stress, fast-paced world, chronic sleep deprivation and insomnia have become epidemic, often linked to deficiencies in essential minerals. Magnesium, often referred to as “nature’s relaxant,” plays a pivotal role in over 300 biochemical reactions in the human body, with its calming effects on the nervous system being arguably the most profound for nighttime recovery.
This comprehensive guide will rigorously explore the biological mechanisms by which magnesium orchestrates sleep, distinguish between the various forms of magnesium (and which are best for sleep), provide evidence-based dosage protocols, and detail the complete clinical picture of utilizing this powerful mineral to conquer restless nights and achieve lasting tranquility.
The Mechanism: How Magnesium Regulates Your Sleep Cycle
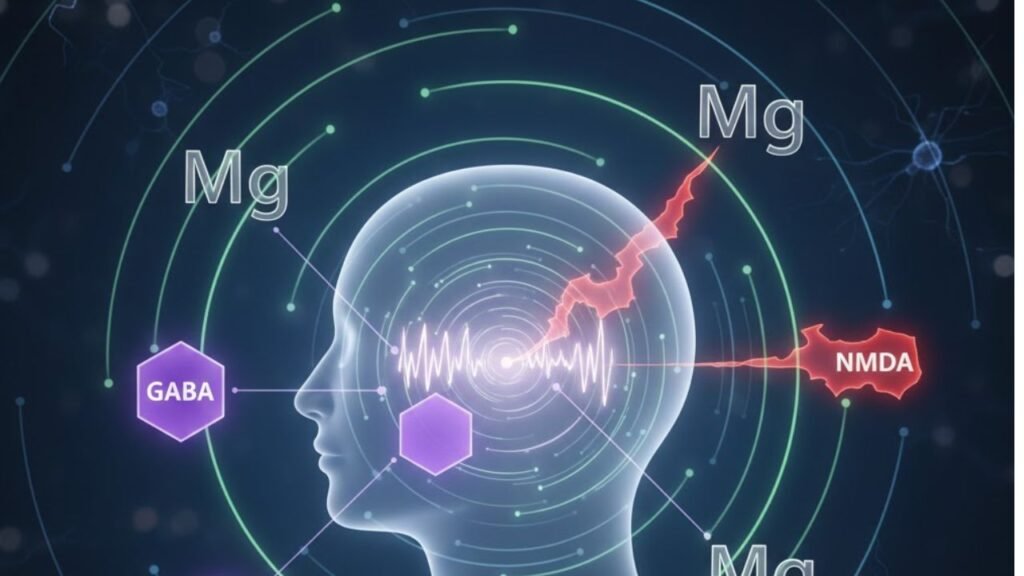
The efficacy of magnesium as a natural sleep aid stems from its direct interaction with key brain functions and hormonal systems responsible for regulating the sleep-wake cycle. The primary target is the GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) system. GABA is the brain’s chief inhibitory neurotransmitter—it acts like a brake pedal on the nervous system, quieting overactive neurons, reducing nerve activity, and promoting deep relaxation.
Magnesium directly binds to and activates GABA receptors in the brain. By boosting GABA activity, magnesium effectively calms the nervous system, reduces levels of the stress hormone cortisol, and prepares the brain for sleep. Furthermore, magnesium helps regulate melatonin production, the hormone that signals to the body that it is time to sleep, and it blocks the excitatory neurotransmitter NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate), further contributing to a state of calm. Addressing a magnesium deficiency is often the missing link for individuals suffering from sleep maintenance insomnia (waking up in the middle of the night).
Choosing the Right Form: Glycinate, Threonate, and More
Not all magnesium supplements are created equal, especially when targeting sleep improvement. The type of magnesium salt used determines its absorption rate (bioavailability) and its primary action within the body. Choosing the wrong form can result in poor results or unwanted side effects (like laxative effects).
The gold standard for promoting relaxation and sleep is Magnesium Glycinate. This form is a chelate, meaning magnesium is bound to the amino acid glycine. Glycine is a calming neurotransmitter itself, and this binding makes the compound highly absorbable while minimizing the risk of digestive side effects. For sleep-specific applications, this is the form most recommended by clinicians.
Magnesium L-Threonate is a newer, highly specialized form engineered to cross the blood-brain barrier effectively. While more research is emerging, it is often favored for cognitive benefits and deep rest due to its ability to increase magnesium concentration directly in the brain.
Magnesium Oxide and Magnesium Citrate, while common, are generally poor choices for sleep therapy. Oxide has low bioavailability, and Citrate is primarily used as a mild osmotic laxative, which can disrupt sleep instead of promoting it.
Your Path to Deeper Sleep and Relaxation
To achieve the best results, it is crucial to use a high-quality, bioavailable form of magnesium. We highly recommend seeking out a supplement that uses Magnesium Glycinate, as it combines maximum calming effects with superior digestive tolerance. Consistent, daily use in the evenings is the key to resetting your body’s natural relaxation response.
Recommended Natural Remedy: High-Absorption Magnesium Glycinate Supplement
[AMAZON LINK: High-Absorption Magnesium Glycinate Supplement (Check Price and Reviews)]
Beyond Sleep: The Role of Magnesium in Stress and Anxiety
The calming effect of magnesium for sleep is directly related to its ability to mitigate daily stress and anxiety. Chronic stress depletes magnesium levels, creating a negative feedback loop where low magnesium exacerbates anxiety, which in turn hinders sleep. Supplementing with magnesium can break this cycle by stabilizing mood and improving resilience to stress.
This effect has been observed in various clinical settings. By supporting GABA function, magnesium helps maintain equilibrium in the nervous system, making it an essential nutrient not just for falling asleep, but for maintaining a balanced emotional state throughout the day.
[clinical study on Magnesium and anxiety reduction from a reputable medical journal]Dosage Protocols and Safety
For an adult, the recommended daily therapeutic dose for sleep typically ranges from 200 mg to 400 mg of elemental magnesium, taken 30-60 minutes before bedtime. It is always best to start at the lower end of the dose and gradually increase until optimal effect is achieved. Magnesium is generally safe, but excessive intake can cause diarrhea or gastrointestinal discomfort. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have existing kidney conditions.
- The Best Herbal Teas for Calming Your Mind Before Bed